Retirement age statistics sets the stage for this enthralling narrative, offering readers a glimpse into a story that is rich in detail and brimming with originality from the outset. As we delve into the fascinating world of retirement age trends, disparities, and industry-specific insights, get ready to uncover the intriguing dynamics that shape this crucial aspect of people’s lives.
Overview of Retirement Age Statistics
In recent years, retirement age statistics have been a topic of interest globally, reflecting shifting trends in workforce demographics and economic conditions. Let’s delve into the history of retirement age trends, factors influencing variations, and a comparison between developed and developing nations.
History of Retirement Age Trends
The concept of retirement as we know it today originated in Germany in the late 19th century with the introduction of the world’s first state pension system. Since then, retirement age has evolved significantly, with many countries gradually increasing the official age of retirement in response to longer life expectancies and financial sustainability of pension systems.
Factors Influencing Retirement Age Variations
Various factors contribute to the variations in retirement age across different countries. These include socio-economic conditions, cultural norms, government policies, life expectancy, and the availability of social security benefits. Developed nations often have higher retirement ages due to longer life expectancies and the need to sustain pension systems, while developing nations may have lower retirement ages influenced by factors like lower life expectancies and less robust social security systems.
Comparison of Retirement Age between Developed and Developing Nations
When comparing retirement age statistics between developed and developing nations, it is evident that developed countries tend to have higher retirement ages. For example, countries like the United States, Germany, and Japan have retirement ages ranging from 65 to 67 years. In contrast, developing nations like India and Brazil often have lower retirement ages, typically around 60 years. These differences highlight the complex interplay of social, economic, and demographic factors shaping retirement age policies globally.
Retirement Age by Country
In different countries around the world, retirement age limits vary based on government regulations, cultural norms, and economic factors. Let’s take a look at how retirement age is determined in countries like the US, Germany, Japan, and Australia.
Retirement Age Limits in Key Countries
In the United States, the full retirement age for Social Security benefits is currently set at 66 years and 2 months for those born in 1955 and gradually increases to 67 for those born in 1960 or later. In Germany, the statutory retirement age is 67, but individuals can choose to retire earlier with reduced benefits. Japan has been gradually increasing its retirement age, with plans to raise it to 65 by 2025. Australia has a retirement age of 67 for those born after 1957.
Impact of Cultural Norms on Retirement Age Decisions
In countries like France, there is a strong cultural emphasis on work-life balance and leisure time, leading to earlier retirement ages. In contrast, China has been increasing its retirement age due to an aging population and economic concerns. Italy faces challenges with an aging workforce and has been considering raising the retirement age to address pension sustainability.
Recent Changes in Retirement Age
Several countries have proposed adjustments to retirement age in response to changing demographics and economic conditions. For example, the US has been discussing potential changes to Social Security benefits to address funding issues. Germany has implemented gradual increases in retirement age to ensure the sustainability of its pension system. Japan has been reevaluating its retirement age policies to accommodate a growing elderly population.
Gender Disparities in Retirement Age
Gender disparities in retirement age are a significant issue that affects men and women worldwide. While retirement age varies by country and individual circumstances, there are noticeable differences between the retirement ages of men and women.
Factors Contributing to Gender Disparities in Retirement Age
- Historical gender roles: Traditional gender roles have often led to women taking on more caregiving responsibilities, resulting in interrupted career paths and lower retirement savings.
- Gender pay gap: The persistent gender pay gap means that women generally earn less than men over their lifetimes, leading to smaller retirement savings and later retirement ages.
- Longer life expectancy for women: Women tend to live longer than men, which means they need to stretch their retirement savings over a longer period, prompting some women to delay retirement.
Initiatives to Address Gender Gaps in Retirement Age
- Equal pay initiatives: Efforts to close the gender pay gap can help ensure that women have the financial means to retire at the same age as men.
- Flexible work arrangements: Providing flexible work options can help women balance work and caregiving responsibilities, allowing them to stay in the workforce longer and save more for retirement.
- Financial literacy programs: Educating women about the importance of saving for retirement and how to invest wisely can help bridge the gender gap in retirement savings.
Retirement Age Trends by Industry
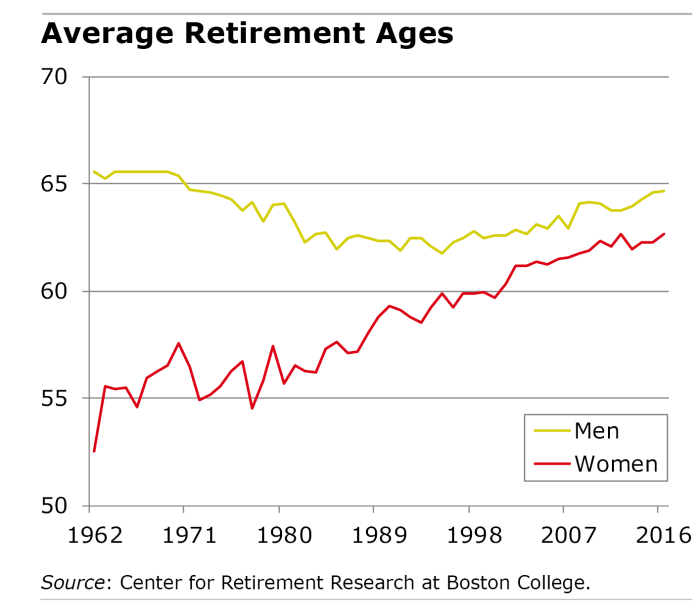
In today’s workforce, retirement age trends can vary significantly across different industries. Factors such as job demands, skill requirements, and company policies play a crucial role in determining when employees choose to retire.
Healthcare Sector
In the healthcare industry, where physical demands are high and specialized skills are required, employees tend to retire later compared to other sectors. Nurses, doctors, and other healthcare professionals often continue working well into their late 60s or even early 70s. This trend is influenced by the shortage of skilled workers in the healthcare field and the increasing demand for quality care.
Technology Industry
On the other hand, the technology sector sees a different retirement age trend. With rapid advancements in technology and the need for up-to-date skills, tech professionals may choose to retire earlier to pursue other interests or ventures. Companies in the tech industry often offer attractive retirement packages to encourage early retirement and make room for younger talent.
Finance Sector
In the finance industry, where expertise and experience are highly valued, employees may choose to work well past the traditional retirement age. Financial advisors, analysts, and executives often continue working into their 70s or even beyond. Companies in the finance sector recognize the value of experienced professionals and implement strategies to retain them for as long as possible.
Manufacturing Sector
The manufacturing industry typically has a mix of retirement age trends. While some employees choose to retire early due to physical demands and repetitive tasks, others continue working into their late 60s or beyond. Companies in the manufacturing sector have implemented various strategies such as flexible work schedules, health and wellness programs, and skills training to extend employees’ working years.
