With Understanding wealth inequality at the forefront, this paragraph opens a window to an amazing start and intrigue, inviting readers to embark on a storytelling journey filled with unexpected twists and insights.
Exploring the complexities of wealth distribution and its impact on society is like uncovering hidden treasures in a modern-day treasure hunt.
Factors contributing to wealth inequality
Wealth inequality is a complex issue influenced by various economic, social, and political factors. Understanding these factors is crucial in addressing and mitigating wealth disparities.
Economic Factors
- Educational disparities: Higher education often leads to better job opportunities and higher income, widening the wealth gap between those with and without advanced degrees.
- Income inequality: Disproportionate distribution of income, with the wealthiest individuals earning significantly more than the average population, contributes to wealth inequality.
- Access to financial resources: Limited access to financial services, such as banking and investment opportunities, can hinder wealth accumulation for certain groups.
- Asset ownership: Disparities in property and asset ownership, including stocks, real estate, and businesses, play a significant role in wealth distribution.
Social Factors
- Historical discrimination: Systemic inequalities based on race, gender, and ethnicity have long-lasting effects on wealth accumulation for marginalized groups.
- Family wealth and inheritance: Intergenerational transfers of wealth can perpetuate inequality, as those born into affluent families have a financial advantage over others.
- Geographic disparities: Disparities in economic opportunities and resources based on location can impact an individual’s ability to accumulate wealth.
Political Decisions
- Tax policies: Progressive or regressive tax structures can either alleviate or exacerbate wealth inequality, depending on how they redistribute wealth among different income groups.
- Social welfare programs: The presence or absence of robust social safety nets can impact wealth distribution by providing support to those in need or further concentrating wealth among the affluent.
- Regulatory framework: Government regulations on industries, labor markets, and financial institutions can either level the playing field or create barriers that perpetuate wealth inequality.
Effects of wealth inequality on society
When wealth is concentrated in the hands of a few, it can have profound effects on society as a whole. Access to essential services like healthcare and education can be severely impacted, leading to a cycle of poverty and inequality that is difficult to break.
Impact on Access to Healthcare and Education
One of the most significant consequences of wealth inequality is the unequal access to healthcare and education. Wealthier individuals have the means to afford quality healthcare and education, while those with lower incomes struggle to access basic services. This disparity can lead to a wide range of negative outcomes, including poorer health outcomes and limited educational opportunities for those in lower socioeconomic brackets.
Relationship with Crime Rates
Studies have shown a direct correlation between wealth inequality and crime rates. When individuals feel marginalized and unable to climb the socioeconomic ladder, they may turn to crime as a means of survival or to address feelings of injustice. This can lead to higher rates of property crime, violent crime, and social unrest in communities with significant wealth disparities.
Psychological Effects of Living in a Society with High Wealth Inequality
The psychological impact of living in a society with high wealth inequality can be profound. Individuals in lower socioeconomic brackets may experience feelings of inadequacy, shame, and hopelessness as they compare themselves to wealthier individuals. This can lead to mental health issues such as depression, anxiety, and low self-esteem, perpetuating a cycle of poverty and inequality.
Historical perspectives on wealth inequality
In order to understand wealth inequality, it is crucial to examine how wealth distribution has evolved over different historical periods. Various factors such as colonization and industrialization have played significant roles in shaping current wealth disparities.
Evolution of Wealth Distribution
- Throughout history, wealth distribution has been heavily influenced by societal structures and power dynamics.
- Feudal systems in the Middle Ages concentrated wealth in the hands of the nobility, leading to vast disparities between the rich and the poor.
- The advent of capitalism during the Industrial Revolution further exacerbated wealth inequality, as industrialists amassed fortunes while workers faced harsh living conditions.
Role of Colonization
- Colonial powers exploited resources and labor in colonized territories, enriching themselves at the expense of indigenous populations.
- This legacy of colonization has contributed to the wealth disparities seen today, as former colonies continue to struggle with economic inequality.
Impact of Industrialization
- The Industrial Revolution transformed economies and societies, creating new opportunities for wealth accumulation.
- However, industrialization also led to the rise of monopolies and income inequality, as a small elite profited greatly while many others struggled to make ends meet.
Solutions to address wealth inequality
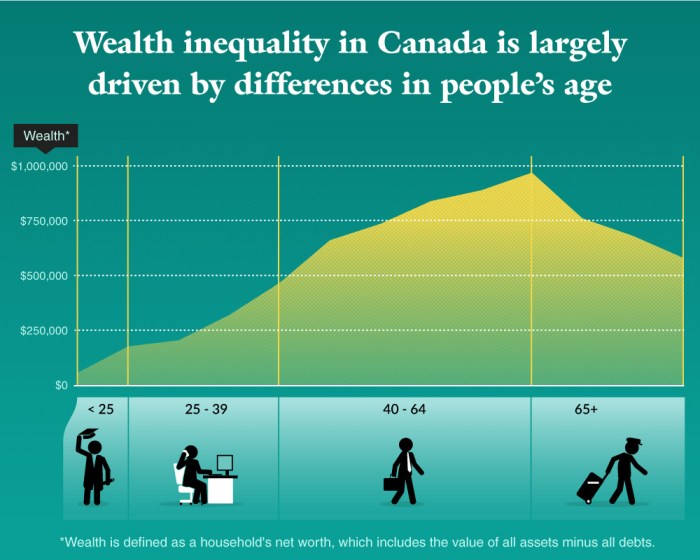
One of the key aspects to reducing wealth inequality is through implementing policy changes that focus on wealth redistribution, improving access to education and skill development opportunities, and promoting economic growth.
Policy Changes for Wealth Redistribution
- Implementing progressive tax policies that tax the wealthy at higher rates to redistribute wealth to lower-income individuals.
- Enforcing regulations on corporate practices to prevent monopolies and ensure fair competition in the market.
- Increasing the minimum wage to provide a living wage for all workers.
Wealth Redistribution Strategies
- Universal Basic Income (UBI) can provide a fixed income to all citizens, regardless of their employment status.
- Implementing wealth taxes on assets such as property, stocks, and inheritance to reduce wealth concentration among the ultra-rich.
- Expanding social welfare programs to provide support for those in need, such as healthcare, housing, and food assistance.
Role of Education and Skill Development
Investing in education and skill development is crucial in narrowing the wealth gap by providing individuals with the tools and knowledge to succeed in the workforce.
- Offering free or affordable higher education and vocational training programs to ensure equal opportunities for all individuals.
- Promoting lifelong learning programs to upskill and reskill workers in response to changing market demands.
- Providing financial literacy education to empower individuals to make informed decisions about their finances and investments.
