Understanding Sales Cycles dives into the dynamic world of sales strategies, offering a glimpse into how businesses can boost their revenue and streamline their operations. From unraveling the stages of a sales cycle to exploring effective management techniques, this topic is a game-changer for companies aiming to stay ahead of the curve.
What is a Sales Cycle
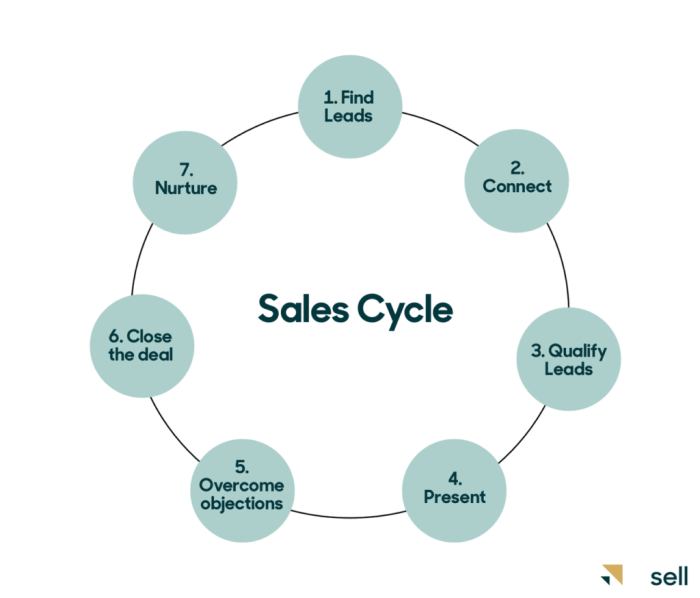
In the world of sales, a sales cycle refers to the process that a company goes through to close a deal with a customer. It involves multiple stages that help guide the sales team from prospecting to closing the sale.
Stages of a Typical Sales Cycle
- Prospecting: This is the stage where potential customers are identified and the sales team reaches out to them to gauge their interest.
- Qualification: In this stage, the leads are evaluated to determine if they are a good fit for the product or service being offered.
- Proposal: The sales team presents a proposal or quote to the prospect, outlining the details of the offer.
- Negotiation: This stage involves back-and-forth discussions to address any concerns or objections the prospect may have.
- Closing: The final stage where the deal is closed, and the customer commits to making a purchase.
Examples of Industries with Varying Sales Cycle Lengths
- Real Estate: The real estate industry typically has a longer sales cycle due to the high value of properties and the extensive decision-making process involved.
- Retail: Retail sales cycles can vary depending on the product being sold, with fast-moving consumer goods having shorter cycles compared to luxury items.
- Software: Software sales cycles can be longer due to the complexity of the products and the need for extensive demonstrations and trials before a purchase decision is made.
Importance of Understanding Sales Cycles
Understanding sales cycles is crucial for businesses as it allows them to anticipate market trends, consumer behavior, and revenue fluctuations. By analyzing sales cycles, companies can make informed decisions, allocate resources effectively, and stay ahead of competitors in the market.
Improving Revenue Forecasting
- Knowledge of sales cycles enables businesses to predict their revenue more accurately. By understanding past sales patterns and trends, companies can forecast future sales with greater precision.
- By recognizing the peak and off-peak periods in their sales cycles, organizations can adjust their strategies accordingly to maximize revenue during high-demand seasons and optimize resources during slower periods.
- Accurate revenue forecasting based on sales cycle analysis helps businesses set realistic targets, manage cash flow more efficiently, and make strategic decisions to drive growth and profitability.
Guiding Marketing Strategies
- Insights from sales cycles can provide valuable information for developing targeted marketing campaigns. By understanding when customers are more likely to make purchases, businesses can tailor their marketing efforts to reach them at the right time with the right message.
- Analyzing sales cycles can help companies identify customer preferences, behaviors, and pain points, allowing them to create personalized marketing strategies that resonate with their target audience and drive engagement.
- By aligning marketing initiatives with the phases of the sales cycle, organizations can optimize their marketing spend, improve customer acquisition and retention, and ultimately enhance their overall sales performance.
Factors Influencing Sales Cycles
Understanding the various factors that influence sales cycles is crucial for businesses to adapt and optimize their strategies for better results.
External Factors Impacting Sales Cycles
- Market Trends: Changes in consumer preferences, economic conditions, and industry trends can directly impact the length of sales cycles.
- Competitive Landscape: The level of competition in the market can influence how quickly or slowly a sale progresses, as businesses may need to adjust their approach to stand out.
- Regulatory Environment: Legal requirements, policies, and regulations can introduce delays or speed up sales cycles depending on how companies navigate compliance issues.
Internal Factors Affecting Sales Cycle Efficiency, Understanding Sales Cycles
- Sales Team Effectiveness: The skills, experience, and motivation of the sales team play a significant role in how efficiently they can move prospects through the sales process.
- Lead Generation Quality: The quality of leads generated by marketing efforts can impact the ease and speed of conversion, as well-qualified leads are more likely to convert quickly.
- Internal Processes: The efficiency of internal processes, such as CRM systems, sales workflows, and communication channels, can streamline or hinder the sales cycle.
Impact of Market Conditions on Sales Cycles
- Boom vs. Recession: During economic booms, sales cycles may shorten due to increased consumer spending, while during recessions, cycles may lengthen as buyers become more cautious.
- Seasonal Variations: Seasonal demand fluctuations can affect the duration of sales cycles, requiring businesses to adjust their strategies accordingly to capitalize on peak periods.
- Emerging Technologies: Adoption of new technologies and digital tools can accelerate sales cycles by enabling faster communication and more personalized interactions with prospects.
Strategies for Managing Sales Cycles
To effectively manage sales cycles, it is important to implement strategies that can help shorten the process and increase efficiency.
Best Practices for Shortening Sales Cycles
- Identify and target high-quality leads to focus on potential customers with a higher likelihood of converting.
- Personalize the sales approach by understanding the unique needs and preferences of each prospect.
- Utilize technology and automation tools to streamline processes and reduce manual tasks.
- Offer incentives or discounts to encourage quicker decision-making and close deals faster.
- Implement effective follow-up strategies to stay engaged with prospects and move them through the sales funnel efficiently.
Describe How CRM Systems Can Streamline and Optimize Sales Cycles
CRM (Customer Relationship Management) systems are essential tools for managing sales cycles effectively. These systems help businesses organize and track interactions with prospects and customers, centralize customer data, automate tasks, and provide insights for making informed decisions. By utilizing CRM systems, sales teams can improve communication, increase productivity, and shorten sales cycles by identifying key touchpoints and focusing on the most effective strategies for closing deals.
Provide Examples of Successful Sales Cycle Management Techniques
- Implementing lead scoring models to prioritize leads based on their likelihood to convert.
- Creating personalized email campaigns that target specific customer segments and address their pain points.
- Utilizing data analytics to track sales performance, identify bottlenecks, and make data-driven decisions to optimize the sales process.
- Establishing clear sales milestones and checkpoints to track progress and ensure timely follow-ups with prospects.
- Training sales teams on effective negotiation techniques and objection handling to overcome hurdles and close deals efficiently.
