Diving into the world of growth vs value stocks, this introductory paragraph aims to grab the attention of readers with a mix of excitement and curiosity.
Exploring the characteristics, factors, and historical performance of these stocks, we’ll uncover the secrets behind their investment potential.
Growth vs Value Stocks Overview
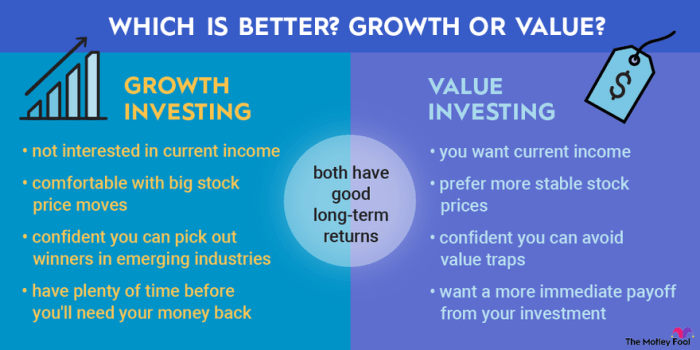
When it comes to investing in stocks, there are two main categories that investors often consider: growth stocks and value stocks. Each type has its own set of characteristics and appeal to different types of investors.
Growth stocks are shares of companies that are expected to grow at a rate above the average market growth. These companies typically reinvest their earnings into expanding their business, developing new products, or entering new markets. They tend to have high price-to-earnings (P/E) ratios and are often considered riskier investments due to their potential for high volatility.
On the other hand, value stocks are shares of companies that are considered undervalued by the market. These companies are often more established and have stable earnings. Value investors look for stocks that are trading below their intrinsic value, based on factors such as earnings, dividends, and book value. They tend to have lower P/E ratios and are seen as more conservative investments.
Main Differences Between Growth and Value Stocks
- Growth stocks focus on companies with high growth potential, while value stocks focus on undervalued companies with stable earnings.
- Growth stocks tend to have high P/E ratios, indicating higher investor expectations, while value stocks have lower P/E ratios, reflecting lower market expectations.
- Growth stocks are considered riskier investments due to their potential for volatility, while value stocks are seen as more conservative investments with lower risk.
- Investors with a higher risk tolerance and a long-term investment horizon may prefer growth stocks, while those seeking stability and income may lean towards value stocks.
Factors Influencing Growth and Value Stocks
When analyzing growth and value stocks, it is important to consider the various factors that can influence their performance. Understanding these key factors can help investors make informed decisions in the stock market.
Growth Stocks
- Growth Potential: Growth stocks are typically companies with high growth potential in terms of revenue, earnings, or market share. Investors are attracted to these stocks for their potential to deliver high returns.
- Market Sentiment: Positive market sentiment and investor optimism can drive up the prices of growth stocks. Conversely, negative sentiment can lead to sharp declines.
- Industry Trends: Growth stocks are often found in industries experiencing rapid technological advancements or disruptive innovations.
- Earnings Growth: Consistent and strong earnings growth is a crucial factor for the performance of growth stocks.
Value Stocks
- Price-to-Earnings Ratio: Value stocks are characterized by lower price-to-earnings ratios compared to growth stocks. Investors look for undervalued companies with strong fundamentals.
- Dividend Yield: Value stocks often pay higher dividends, making them attractive to income-seeking investors.
- Market Cyclicity: Value stocks tend to perform well during economic downturns when investors seek safer, stable investments.
- Asset Value: Value stocks are sometimes backed by tangible assets, providing a margin of safety for investors.
Economic Conditions Impact
- In a booming economy, growth stocks tend to outperform value stocks as investors chase high-growth opportunities.
- During economic downturns, value stocks may fare better as investors prioritize stability and value over growth potential.
Interest Rates
- Low interest rates favor growth stocks as companies can borrow cheaply to fuel expansion and innovation.
- High interest rates may benefit value stocks as investors seek stable companies with solid fundamentals and lower debt levels.
Historical Performance
When comparing the historical performance of growth and value stocks, it is essential to analyze how each category has fared over different market cycles.
Comparison of Historical Performance Trends
- Historically, growth stocks have outperformed value stocks during bull markets due to their strong earnings growth potential and investor optimism.
- On the other hand, value stocks have shown resilience during market downturns, as investors flock to these undervalued assets for stability and potential long-term gains.
- Over the long term, growth stocks tend to have higher volatility but also higher potential returns, while value stocks offer more stable returns with lower risk.
Impact of Market Cycles
- During bull markets, growth stocks tend to shine as investors seek high-growth companies with promising future prospects.
- Conversely, value stocks may lag behind during bull markets as they are often overlooked in favor of more glamorous growth opportunities.
- However, during bear markets or economic downturns, value stocks have historically shown more resilience and tend to outperform growth stocks due to their lower valuation multiples and strong fundamentals.
Risk and Volatility
Investing in both growth and value stocks comes with its own set of risks and levels of volatility. Understanding these factors is crucial for making informed investment decisions.
Risk Levels Associated with Growth Stocks
- Growth stocks are often considered riskier because they typically trade at higher valuations compared to their current earnings. This means that any negative news or changes in the market sentiment can lead to significant price fluctuations.
- These stocks are usually more sensitive to economic downturns or changes in interest rates, making them vulnerable to market corrections.
- Investors in growth stocks are also exposed to company-specific risks such as the failure to meet growth expectations, product development delays, or increased competition.
Risk Levels Associated with Value Stocks
- Value stocks are often perceived as less risky because they trade at lower valuations relative to their fundamentals, such as earnings, assets, or cash flow.
- However, these stocks can still be subject to risks such as poor management decisions, industry-specific challenges, or unexpected regulatory changes.
- Value stocks may also underperform during periods of economic growth or market exuberance, as investors flock to higher-growth opportunities.
Comparing Volatility of Growth and Value Stocks
- Growth stocks tend to exhibit higher volatility compared to value stocks due to their sensitivity to market conditions and earnings expectations.
- Value stocks, on the other hand, may experience lower volatility as they are often seen as more stable and less susceptible to rapid price swings.
- During market downturns, growth stocks may experience sharper declines, while value stocks could provide more stability and potentially outperform in such environments.
Investment Strategies
When it comes to investing in growth and value stocks, different strategies can be employed to maximize returns and manage risks effectively.
Investment Strategies for Growth Stocks
- Focus on companies with high potential for earnings growth: Look for companies in industries that are expected to grow rapidly and have a competitive edge.
- Invest in disruptive technologies: Identify companies that are innovating and disrupting traditional industries, as they have the potential for significant growth.
- Monitor revenue and earnings growth: Regularly track the financial performance of growth stocks to ensure they are meeting growth expectations.
- Consider long-term investment horizon: Growth stocks may require patience as the companies reinvest earnings for future growth, so a long-term perspective is essential.
Investment Strategies for Value Stocks
- Look for undervalued companies: Identify companies that are trading below their intrinsic value based on fundamental analysis.
- Focus on dividend-paying stocks: Consider value stocks that pay dividends, as they can provide a source of income and potentially offer downside protection.
- Invest in out-of-favor sectors: Explore industries that are currently out of favor or facing temporary challenges, as they may offer value opportunities.
- Monitor price-to-earnings and price-to-book ratios: Use valuation metrics to assess whether a value stock is truly undervalued compared to its peers.
Diversification in Growth and Value Stocks
Diversification is crucial when investing in growth and value stocks to mitigate risks and optimize returns. By spreading your investments across different sectors, industries, and market caps, you can reduce the impact of any single stock’s performance on your overall portfolio. Diversification helps balance the potential high returns of growth stocks with the stability and value proposition of value stocks, creating a well-rounded investment approach.
