Dive into the world of financial strategy with our guide on how to leverage debt. Discover the art of using debt to your advantage, maximizing returns, and achieving your goals in a whole new way.
Learn about the different types of debt, the benefits and risks involved, and the key strategies to effectively leverage debt for success.
Introduction to Leveraging Debt
Debt leveraging is a financial strategy where individuals or businesses borrow money to invest in assets or projects with the goal of increasing returns. By using debt to finance investments, the hope is that the returns generated will outweigh the cost of borrowing, resulting in a profit.
Benefits of Leveraging Debt
- Increased Investment Potential: Leveraging debt allows individuals or businesses to invest in assets they may not have been able to afford otherwise, potentially leading to higher returns.
- Tax Advantages: In some cases, the interest paid on debt used for investments may be tax-deductible, reducing the overall tax liability.
- Asset Diversification: Leveraging debt can help diversify investment portfolios by spreading risk across different asset classes.
Types of Debt for Leveraging
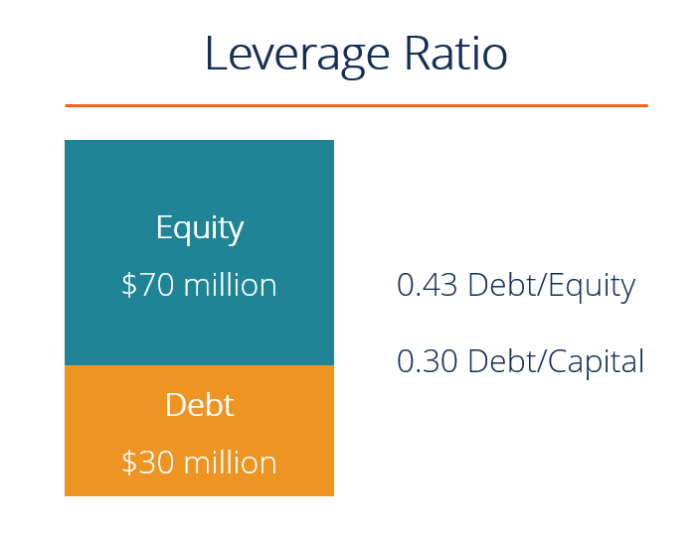
When it comes to leveraging debt, there are several types that can be utilized strategically to achieve financial goals. Understanding the characteristics of each type of debt is crucial in making informed decisions.
Credit Card Debt
- Credit card debt is unsecured debt that comes with high-interest rates.
- It can be used strategically for leveraging by taking advantage of rewards programs or cashback offers.
- However, carrying a balance on credit cards can lead to significant interest charges, so it should be managed carefully.
Mortgage Debt
- Mortgage debt is secured debt that is used to finance the purchase of a home.
- It can be leveraged strategically by taking advantage of tax deductions on mortgage interest payments.
- Additionally, the value of the property may appreciate over time, providing a return on investment.
Student Loan Debt
- Student loan debt is used to finance education and is typically considered good debt due to potential future earning potential.
- It can be leveraged strategically by investing in further education or skill development to increase earning potential.
- However, high levels of student loan debt can impact other financial goals, so it should be managed wisely.
Benefits of Leveraging Debt
When it comes to financial strategies, leveraging debt can offer various advantages that can help individuals and businesses achieve their goals more effectively.
Increased Financial Flexibility
One of the key benefits of leveraging debt is the ability to increase financial flexibility. By using borrowed funds, individuals or businesses can access additional capital to invest in opportunities, expand operations, or weather financial challenges.
Enhanced Return on Investment
Compared to using only your own funds, leveraging debt can potentially lead to a higher return on investment. By borrowing money at a lower interest rate than the return on the investment, you can amplify your gains and grow your wealth more rapidly.
Tax Benefits
Debt financing often comes with tax advantages that can help reduce the overall tax burden. Interest payments on loans are typically tax-deductible, providing a way to lower taxable income and potentially increase cash flow.
Example: Real Estate Investment
One common example of successful leveraging of debt is in real estate investment. By taking out a mortgage to purchase a property, investors can benefit from appreciation in property value, rental income, and tax advantages while using relatively little of their own capital.
Risks and Challenges of Leveraging Debt
When it comes to leveraging debt, there are certain risks and challenges that individuals or businesses need to be aware of in order to make informed decisions. Understanding these risks is crucial to avoid financial pitfalls and ensure successful debt leveraging strategies.
Interest Rate Fluctuations
One of the main risks of leveraging debt is the impact of interest rate fluctuations. If interest rates rise unexpectedly, the cost of servicing the debt can increase significantly, putting strain on the borrower’s finances. To mitigate this risk, individuals can consider fixed-rate loans or hedge against interest rate changes.
Overleveraging
Overleveraging occurs when an individual or business takes on too much debt relative to their assets or income. This can lead to financial instability and difficulty in meeting debt obligations. To prevent overleveraging, it’s important to carefully assess one’s financial situation and borrowing capacity before taking on additional debt.
Market Volatility
Market volatility can also pose a risk when leveraging debt, especially for investments or businesses that are sensitive to market fluctuations. To manage this risk, individuals can diversify their investments, maintain a liquid emergency fund, and stay informed about market trends.
Default Risk
Default risk is the risk that a borrower may be unable to repay the debt as agreed, leading to potential legal action or credit damage. To mitigate default risk, borrowers should ensure they have a solid repayment plan in place, maintain a good credit score, and communicate with lenders if facing financial difficulties.
Strategies for Effective Debt Leverage
When it comes to effectively leveraging debt, there are key strategies that individuals and businesses can implement to maximize the benefits while minimizing the risks. Developing a solid debt leveraging strategy requires careful consideration and planning to ensure success. Here, we will discuss some important strategies and provide a step-by-step guide on how to implement a debt leveraging plan.
Key Strategies for Effective Debt Leverage
- Assess your current financial situation: Before taking on any debt, it’s essential to evaluate your current financial position. Understand your income, expenses, assets, and liabilities to determine how much debt you can comfortably afford.
- Set clear financial goals: Define your financial objectives and how leveraging debt can help you achieve them. Whether it’s expanding your business, investing in real estate, or funding education, having clear goals will guide your debt leveraging strategy.
- Diversify your debt portfolio: Avoid putting all your eggs in one basket by diversifying the types of debt you take on. Consider a mix of long-term loans, short-term credit lines, and other financing options to spread out risk.
- Negotiate favorable terms: When borrowing money, negotiate with lenders for the best possible terms, including interest rates, repayment schedules, and collateral requirements. A lower interest rate can save you significant money in the long run.
- Monitor and manage debt effectively: Stay on top of your debt obligations by tracking payments, managing cash flow, and making timely repayments. Avoid accumulating more debt than you can handle and prioritize paying off high-interest loans first.
Considerations when Developing a Debt Leveraging Strategy
It’s crucial to consider your risk tolerance, cash flow projections, and the purpose of borrowing when developing a debt leveraging strategy.
Step-by-Step Guide on Implementing a Debt Leveraging Plan
- Evaluate your financial goals and borrowing needs.
- Research and compare different borrowing options.
- Create a detailed budget and repayment plan.
- Negotiate terms with lenders and secure favorable agreements.
- Implement your debt leveraging plan and monitor progress regularly.
