Diving into the world of Interest rates and mortgages, we uncover the intricate dance between these financial elements that shape the housing market. As we navigate through the complexities, a story unfolds that sheds light on the impact of interest rates on mortgage affordability and the housing sector as a whole.
Exploring the relationship between interest rates and mortgages reveals a dynamic landscape where economic indicators, central bank policies, and market conditions play a pivotal role in shaping the financial decisions of many.
Overview of Interest Rates and Mortgages
Interest rates and mortgage rates have a close relationship. Mortgage rates are influenced by interest rates set by the Federal Reserve. When interest rates are low, mortgage rates tend to be lower as well, making it more affordable for people to borrow money to buy a home.
Impact of Interest Rates on Mortgage Affordability
- Lower interest rates mean lower monthly mortgage payments, making homeownership more accessible to a wider range of people.
- Higher interest rates result in higher monthly mortgage payments, potentially pricing some buyers out of the market.
- Changes in interest rates can also affect the overall cost of borrowing, impacting the total amount paid over the life of the loan.
Effects of Interest Rate Changes on the Housing Market
- When interest rates are low, more people are motivated to buy homes, leading to increased demand and potentially driving up housing prices.
- Conversely, when interest rates rise, demand for homes may decrease as borrowing becomes more expensive, potentially causing a slowdown in the housing market.
- Fluctuations in interest rates can also impact the number of homes sold, new constructions, and overall economic activity related to the housing market.
Types of Mortgages
When it comes to mortgages, there are two main types to consider: fixed-rate mortgages and adjustable-rate mortgages. Each type has its own set of pros and cons, especially when it comes to interest rates.
Fixed-Rate Mortgages
A fixed-rate mortgage has an interest rate that remains the same for the entire term of the loan. This means your monthly payments will also stay constant, providing predictability and stability in budgeting. However, fixed-rate mortgages typically have slightly higher interest rates compared to adjustable-rate mortgages.
Adjustable-Rate Mortgages
On the other hand, an adjustable-rate mortgage (ARM) has an interest rate that can fluctuate over time based on market conditions. Initially, ARMs often offer lower interest rates compared to fixed-rate mortgages, making them attractive to borrowers looking for lower initial payments. However, the interest rate can change periodically, leading to potential fluctuations in monthly payments.
Interest Rates Influence Mortgage Choice
The choice between a fixed-rate mortgage and an adjustable-rate mortgage is heavily influenced by current interest rates. When interest rates are low, borrowers may opt for a fixed-rate mortgage to lock in a favorable rate for the long term. In contrast, when interest rates are high, borrowers may consider an adjustable-rate mortgage to take advantage of potential future rate decreases.
Factors Influencing Interest Rates
Interest rates are influenced by various factors that impact the overall economy and financial markets. Understanding these key factors is essential for individuals looking to secure a mortgage at the best possible rate.
Economic Indicators
Economic indicators such as GDP growth, unemployment rates, and consumer spending play a significant role in determining interest rates. A strong economy typically leads to higher interest rates as demand for loans increases.
Central Bank Policies
Central banks, such as the Federal Reserve in the United States, have the power to influence interest rates through their monetary policy decisions. By adjusting the federal funds rate, central banks can directly impact short-term interest rates, which in turn affect mortgage rates.
Inflation
Inflation is another crucial factor that influences interest rates. When inflation rates rise, lenders demand higher interest rates to compensate for the decrease in purchasing power over time. Conversely, low inflation rates may lead to lower interest rates on mortgages.
Credit Scores
Credit scores are a key determinant of the interest rates borrowers receive on their mortgages. Individuals with higher credit scores are seen as less risky by lenders and are therefore offered lower interest rates. On the other hand, borrowers with lower credit scores may face higher interest rates to offset the perceived risk.
Market Conditions
Market conditions, including supply and demand for mortgage-backed securities, also impact interest rates. During times of economic uncertainty or market volatility, lenders may increase rates to mitigate risk. Conversely, in a stable market with high demand for loans, interest rates may be more competitive.
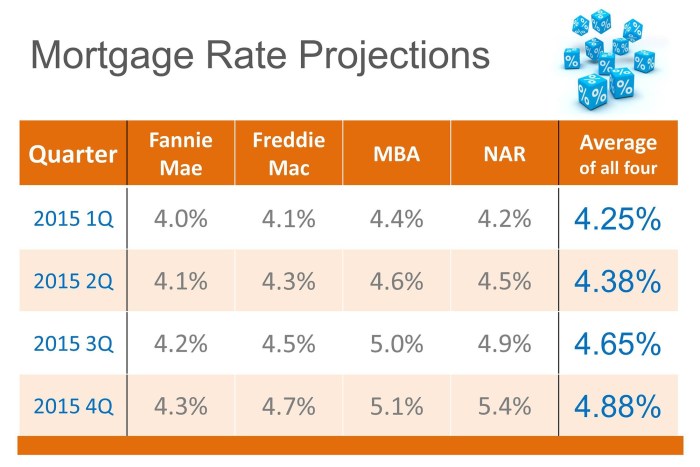
Mortgage Rate Trends
In the world of mortgages, keeping an eye on the trends of interest rates is crucial for potential homebuyers. Let’s dive into the historical data of mortgage rate trends over the past decade and see how they have responded to various economic events.
Decade-long Mortgage Rate Trends
- 2009-2012: In the aftermath of the 2008 financial crisis, mortgage rates hit record lows as the Federal Reserve implemented quantitative easing measures to stimulate the economy.
- 2013-2016: Mortgage rates remained relatively stable, hovering around historical lows due to the slow economic recovery and low inflation rates.
- 2017-2019: As the economy started to pick up steam, mortgage rates began to gradually rise, influenced by factors such as strong job growth and higher inflation expectations.
- 2020-2021: The onset of the COVID-19 pandemic led to a sharp decline in mortgage rates as the Federal Reserve slashed interest rates to combat the economic impact of the global health crisis.
Monitoring mortgage rate trends can help potential homebuyers make informed decisions on when to lock in a mortgage rate, potentially saving thousands of dollars over the life of a loan.
Calculating Mortgage Payments
When it comes to calculating mortgage payments, it’s essential to consider the loan amount, interest rate, and term of the loan. The monthly payment amount is influenced by these factors, so understanding how they interact is crucial for managing your finances effectively.
Impact of Interest Rates on Monthly Payments
- Higher interest rates result in higher monthly payments: When interest rates go up, the cost of borrowing money increases, leading to higher monthly mortgage payments.
- Lower interest rates mean lower monthly payments: Conversely, lower interest rates translate to lower monthly mortgage payments, making homeownership more affordable.
Strategies for Managing Mortgage Payments
- Refinance your mortgage: If interest rates are rising, consider refinancing your mortgage to secure a lower rate and reduce your monthly payments.
- Make extra payments: Paying more than the minimum monthly amount can help you pay off your mortgage faster and reduce the total interest paid over the life of the loan.
- Adjust your budget: In a rising interest rate environment, it’s essential to review your budget regularly and make necessary adjustments to accommodate higher mortgage payments.
