Diving into Planning for healthcare costs in retirement, this intro sets the stage with a fresh and engaging look at the topic, hitting the sweet spot of interest and relevance.
In this guide, we’ll break down the nitty-gritty details of how to plan for healthcare costs in retirement, giving you the inside scoop on what to expect and how to prepare.
Understanding Healthcare Costs in Retirement
Healthcare costs in retirement refer to the expenses associated with medical care, treatments, and services that retirees need to maintain their health and well-being.
Planning for healthcare costs in retirement is essential to ensure that retirees can afford necessary medical care without depleting their savings or facing financial hardships.
Factors Contributing to Healthcare Costs in Retirement
- Rising healthcare costs: Healthcare expenses tend to increase over time due to inflation, technological advancements, and other factors.
- Health status: Retirees with chronic conditions or complex healthcare needs may incur higher medical expenses.
- Insurance coverage: The type of health insurance plan retirees have and their coverage levels can impact out-of-pocket costs for medical services.
- Long-term care needs: Costs associated with long-term care facilities or in-home care can significantly contribute to healthcare expenses in retirement.
Estimating Healthcare Expenses
Estimating healthcare expenses in retirement is crucial for financial planning. It involves considering various factors such as current health conditions, potential future medical needs, and the rising costs of healthcare services.
Common Healthcare Services and Costs for Retirees
- Doctor visits: Routine check-ups can cost anywhere from $100 to $300 per visit without insurance.
- Prescription medications: Monthly costs for medications can range from $50 to $300 depending on the type and dosage.
- Emergency room visits: A single visit to the ER can cost thousands of dollars, especially if hospitalization is required.
- Medical procedures: Surgeries and specialized treatments can easily add up to tens of thousands of dollars.
It’s important to factor in inflation when estimating healthcare expenses in retirement, as medical costs tend to rise over time.
Health Insurance Options for Retirees
When it comes to health insurance options for retirees, there are several choices available to help cover medical expenses during retirement. Let’s take a look at some of the main options and how they can benefit retirees.
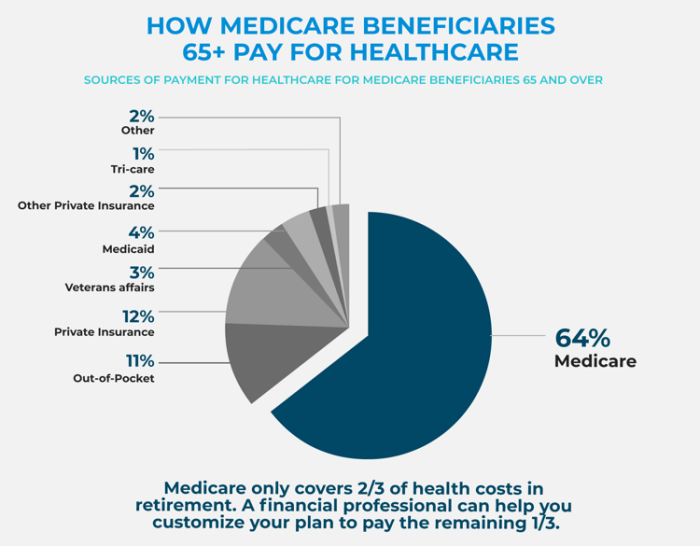
Medicare Coverage
Medicare is a federal health insurance program primarily for individuals aged 65 and older. It consists of several parts, including Part A (hospital insurance) and Part B (medical insurance). While Medicare provides coverage for a wide range of medical services, it does not cover all expenses. It is essential to understand the gaps in Medicare coverage and consider additional insurance options to fill those gaps.
- Medicare Part A: Covers inpatient hospital stays, skilled nursing facility care, hospice care, and some home health care.
- Medicare Part B: Covers certain doctors’ services, outpatient care, medical supplies, and preventive services.
- Medicare Part D: Offers prescription drug coverage through private insurance companies.
It’s important to review your Medicare coverage annually during the open enrollment period to ensure it meets your healthcare needs.
Supplemental Insurance
Supplemental insurance, also known as Medigap, is designed to help cover the costs that Medicare does not pay for, such as copayments, coinsurance, and deductibles. These plans are offered by private insurance companies and can provide additional financial protection for retirees.
- Medigap Plans: Offered by private insurers to cover out-of-pocket costs not covered by Medicare.
- Medicare Advantage Plans: Alternative to original Medicare that often includes additional benefits like vision, dental, and prescription drug coverage.
- Retiree Health Plans: Some employers offer health insurance coverage to retired employees, which can supplement Medicare benefits.
Supplemental insurance can help retirees manage healthcare costs and provide peace of mind by filling the gaps left by Medicare coverage.
Long-Term Care Planning
Long-term care is a crucial aspect of retirement planning as it involves the services needed when someone is unable to care for themselves due to aging, illness, or disability. Planning for long-term care ensures that retirees can maintain their quality of life and avoid financial strain on themselves and their families.
Different Long-Term Care Options and Costs
There are various long-term care options available, each with its associated costs:
- Nursing Homes: Provide 24-hour medical care and assistance with daily activities. Costs can range from $80,000 to $100,000 per year.
- Assisted Living Facilities: Offer a combination of housing, personal care services, and healthcare. Costs can vary from $40,000 to $60,000 annually.
- Home Health Care: Involves receiving care at home by a professional caregiver. Costs can range from $20 to $30 per hour.
Strategies for Incorporating Long-Term Care Costs into Retirement Planning
It is essential to plan ahead for long-term care costs to avoid financial strain in retirement. Here are some strategies to consider:
- Long-Term Care Insurance: Purchase a long-term care insurance policy to help cover the costs of care services.
- Health Savings Account (HSA): Contribute to an HSA to save for future healthcare expenses, including long-term care.
- Medicaid Planning: Understand the eligibility requirements for Medicaid and plan accordingly to potentially cover long-term care costs.
