Retirement account contributions are the key to building a secure financial future, and understanding their ins and outs is crucial for anyone looking to retire comfortably. Get ready to dive into the world of retirement planning with a fresh perspective that’s as cool as your favorite high school hip hop track.
As we explore the different types of retirement accounts, strategies for maximizing contributions, and their impact on retirement age, you’ll be equipped with the knowledge to make smart financial decisions for your golden years.
Importance of Retirement Account Contributions
Saving for retirement is a crucial part of financial planning that can provide a secure future and peace of mind. Regular contributions to retirement accounts help individuals build a nest egg that can sustain them during their golden years. Let’s dive into the benefits and impacts of contributing to retirement accounts.
Benefits of Regular Contributions
- Compound Interest: By contributing regularly, you allow your money to grow through compound interest, maximizing your savings over time.
- Tax Advantages: Retirement account contributions often come with tax benefits, such as tax-deferred growth or tax-free withdrawals in retirement.
- Financial Security: Building a substantial retirement fund through regular contributions ensures you have the financial security to maintain your lifestyle after you retire.
Impact of Early vs. Late Contributions
“The earlier you start contributing to your retirement account, the more time your money has to grow.”
- Early Contributions: Starting to contribute to a retirement account early allows you to take advantage of compounding returns, potentially resulting in a larger nest egg at retirement.
- Late Contributions: While it’s never too late to start saving for retirement, late contributions may not have the same growth potential as early contributions due to the shorter time horizon.
- Retirement Readiness: Early contributions can help ensure you are financially prepared for retirement, while late contributions may require more aggressive saving and investing strategies to catch up.
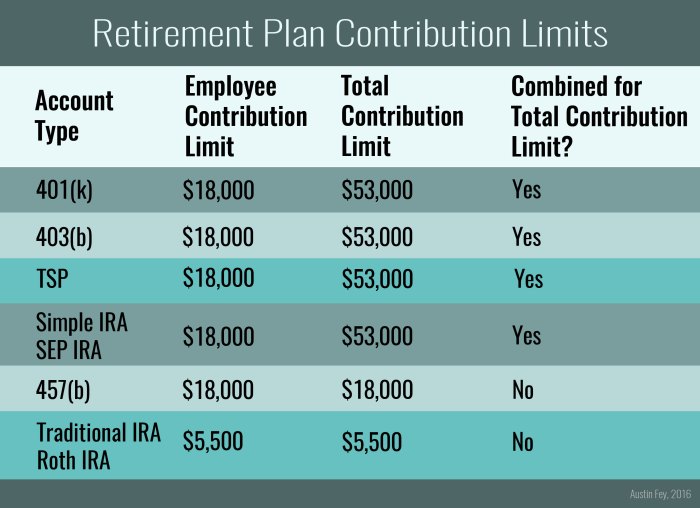
Types of Retirement Accounts
When it comes to saving for retirement, there are several types of retirement accounts to choose from. Each type has its own eligibility criteria and tax implications. Let’s take a closer look at some common retirement accounts:
401(k)
A 401(k) is an employer-sponsored retirement account that allows employees to contribute a portion of their salary to save for retirement. Contributions are typically made on a pre-tax basis, meaning they are not taxed until withdrawn during retirement. Employers may also match a percentage of employee contributions, helping to grow the retirement savings faster.
Traditional IRA
A Traditional IRA is a retirement account that individuals can open on their own, regardless of employer sponsorship. Contributions to a Traditional IRA are often tax-deductible, meaning they can lower taxable income in the year they are made. However, withdrawals in retirement are taxed as ordinary income.
Roth IRA
A Roth IRA is similar to a Traditional IRA, but with a key difference – contributions are made after-tax, meaning they are not tax-deductible. However, the big advantage of a Roth IRA is that withdrawals in retirement are tax-free, including any investment gains.
Strategies for Maximizing Retirement Contributions
When it comes to maximizing your retirement contributions, there are several strategies you can employ to ensure you are saving as much as possible for your future financial security.
Tips for Maximizing Retirement Contributions Annually
- Contribute the maximum amount allowed by your employer-sponsored retirement plan, such as a 401(k) or 403(b).
- Consider setting up automatic contributions from your paycheck to ensure consistent savings.
- Take advantage of employer matching contributions, as this is essentially free money towards your retirement savings.
- Make catch-up contributions if you are over 50 years old to further boost your retirement savings.
The Concept of Catch-Up Contributions
By making catch-up contributions, individuals who are nearing retirement age can contribute additional funds to their retirement accounts beyond the regular annual limits. This allows older individuals to make up for lost time and increase their savings quickly as they approach retirement.
Advantages of Contributing to Multiple Retirement Accounts Simultaneously
- Diversification: Contributing to different types of retirement accounts helps spread out your investments and reduce risk.
- Tax Benefits: Depending on the type of retirement account, you may be able to benefit from different tax advantages by contributing to multiple accounts.
- Increased Savings: By contributing to multiple accounts, you can potentially save more money for retirement than if you were limited to just one account.
Impact of Retirement Account Contributions on Retirement Age
Retirement account contributions play a crucial role in determining the age at which individuals can comfortably retire. By analyzing varying contribution amounts, one can better understand how they affect retirement age and flexibility.
Accelerating Retirement Age Through Strategic Contributions
Strategic retirement account contributions can enable individuals to retire earlier than expected. By maximizing contributions and taking advantage of employer matching programs, some individuals have successfully accelerated their retirement age.
