With Trends in retirement savings at the forefront, this paragraph opens a window to an amazing start and intrigue, inviting readers to embark on a storytelling american high school hip style filled with unexpected twists and insights.
When it comes to retirement savings, staying ahead of the game is crucial. Let’s dive into the latest trends shaping the way we save for our golden years. From innovative technologies to generational perspectives, this topic is a goldmine of information waiting to be explored.
Overview of Retirement Savings Trends
Saving for retirement is a crucial financial goal for many individuals. Let’s take a look at the current trends in retirement savings and the factors influencing them.
Factors Influencing Retirement Savings Trends
- Rising life expectancy: With people living longer, the need for adequate retirement savings has increased.
- Shifting job market: The rise of the gig economy and freelancing has impacted how individuals save for retirement.
- Changes in pension plans: The shift from defined benefit plans to defined contribution plans has placed more responsibility on individuals to save for retirement.
Impact of Economic Conditions on Retirement Savings Patterns
- Market volatility: Economic downturns can negatively impact retirement savings, leading to decreased account balances.
- Interest rates: Low interest rates can affect the growth of retirement savings, making it challenging to achieve long-term financial goals.
- Inflation: High inflation rates can erode the purchasing power of retirement savings over time, necessitating more aggressive saving strategies.
Types of Retirement Savings Accounts
When it comes to saving for retirement, there are several types of accounts you can consider. Each type has its own features, benefits, and limitations that you should be aware of before making a decision.
401(k)
A 401(k) is a retirement savings account typically offered by employers to their employees. One of the key features of a 401(k) is that contributions are made pre-tax, which can help lower your taxable income. Additionally, some employers may match a portion of your contributions, essentially providing free money towards your retirement savings. However, there are limitations on when you can withdraw funds from a 401(k) without facing penalties.
IRA (Individual Retirement Account)
An IRA is a retirement savings account that you can open on your own, outside of an employer-sponsored plan. There are two main types of IRAs: traditional and Roth. With a traditional IRA, contributions are made with pre-tax dollars, similar to a 401(k). On the other hand, a Roth IRA allows for after-tax contributions, but qualified withdrawals in retirement are tax-free. IRAs offer more flexibility in investment choices compared to 401(k) plans.
Roth IRA
A Roth IRA is a type of individual retirement account that offers tax-free growth and withdrawals in retirement. Contributions to a Roth IRA are made with after-tax dollars, meaning you won’t get a tax deduction upfront like with a traditional IRA or 401(k). However, the trade-off is that you can withdraw your contributions (but not earnings) at any time penalty-free. Roth IRAs are especially beneficial for those who expect to be in a higher tax bracket in retirement.
Emerging Technologies in Retirement Savings
Technology is revolutionizing the way we plan for retirement, offering new tools and resources to help individuals secure their financial future. Apps and online platforms are playing a crucial role in simplifying retirement planning, providing easy access to information and tools to track and manage savings. Additionally, the rise of AI and automation is reshaping retirement savings strategies, offering personalized recommendations and automated solutions to optimize savings and investment decisions.
Role of Apps and Online Platforms
Apps and online platforms have made it easier than ever for individuals to access their retirement savings accounts, monitor their investments, and track their progress towards their retirement goals. These tools provide real-time updates, interactive calculators, and educational resources to help users make informed decisions about their savings and investments. By offering a convenient and user-friendly experience, apps and online platforms are empowering individuals to take control of their retirement planning.
Impact of AI and Automation
AI and automation are transforming retirement savings strategies by providing personalized recommendations based on individual goals, risk tolerance, and financial situation. These technologies analyze data, predict market trends, and automate investment decisions to optimize savings and achieve long-term financial goals. By leveraging AI and automation, individuals can benefit from efficient portfolio management, lower fees, and improved investment outcomes, ultimately enhancing their retirement savings strategy.
Generational Perspectives on Retirement Savings
Millennials, Gen X, and Baby Boomers each have unique approaches to retirement savings based on their generational values and financial circumstances.
Baby Boomers
Baby Boomers, born between 1946 and 1964, are nearing retirement age and have traditionally focused on employer-sponsored pension plans and Social Security benefits. Many Baby Boomers are facing challenges such as inadequate savings due to economic downturns and rising healthcare costs.
Gen X
Gen X, born between 1965 and 1980, are known for being independent and entrepreneurial. They prioritize saving for retirement through 401(k) plans and individual retirement accounts (IRAs). However, Gen Xers often struggle to balance saving for retirement with other financial responsibilities like paying off debt and saving for their children’s education.
Millennials
Millennials, born between 1981 and 1996, are early in their careers and face unique challenges such as high student loan debt and lower job security. Despite these obstacles, Millennials are more likely to prioritize retirement savings through employer-sponsored 401(k) plans and Roth IRAs. They also value socially responsible investing and seek financial advice from technology-driven platforms.
Employer-Sponsored Retirement Plans
Employer-sponsored retirement plans are a crucial aspect of retirement savings for many individuals. These plans are typically provided by employers to help their employees save for retirement in a tax-advantaged manner.
Common Types of Employer-Sponsored Retirement Plans
- 401(k) Plans: These are one of the most common types of retirement plans offered by employers. Employees can contribute a portion of their salary to the plan, often with matching contributions from the employer.
- Pension Plans: Also known as defined benefit plans, these plans provide employees with a specific benefit amount upon retirement based on factors such as salary and years of service.
- 403(b) Plans: Similar to 401(k) plans but offered by non-profit organizations, schools, and certain government entities.
- 457 Plans: Available to state and local government employees, these plans allow for tax-deferred contributions towards retirement.
Importance of Employer Contributions to Retirement Savings
Employer contributions to retirement savings can significantly boost an individual’s ability to save for retirement. Matching contributions, profit-sharing, and other employer contributions can help grow retirement savings faster and maximize the benefits of employer-sponsored plans.
Trends in Employer-Sponsored Retirement Plans Adoption
- Automatic Enrollment: Many employers are adopting automatic enrollment features in their retirement plans to increase employee participation.
- Target Date Funds: These funds are becoming more popular in employer-sponsored plans as they automatically adjust the investment mix based on the employee’s age and retirement timeline.
- Financial Wellness Programs: Employers are increasingly offering financial education and wellness programs to help employees better understand and utilize their retirement benefits.
Social Security and Retirement Savings
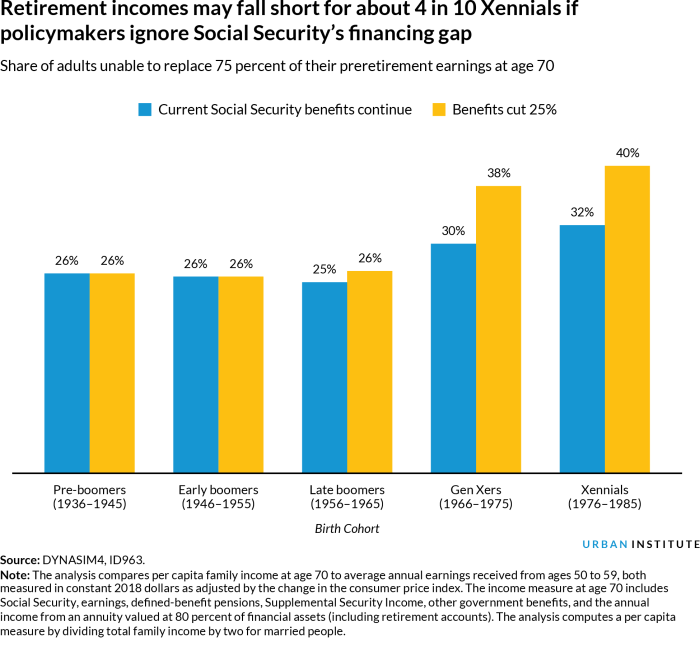
Social Security plays a crucial role in retirement savings for many Americans. It provides a safety net for individuals who have contributed to the system throughout their working years. Understanding how Social Security impacts retirement savings strategies is essential for financial planning.
Role of Social Security
- Social Security provides a steady source of income for retirees, disabled individuals, and survivors of deceased workers.
- It is funded through payroll taxes, with contributions from both employees and employers.
- Benefits are based on a worker’s earnings history and the age at which they choose to start receiving benefits.
Challenges and Future Outlook
- Current challenges facing Social Security include a growing number of retirees compared to the working population, potentially leading to funding shortages.
- There have been discussions about potential reforms to ensure the long-term sustainability of Social Security benefits.
- Future outlooks suggest that adjustments may be required to maintain benefit levels for future generations.
Impact on Retirement Savings Strategies
- Social Security benefits can complement other retirement savings accounts, such as 401(k) plans or IRAs, to provide a more secure financial future.
- Understanding the timing of when to start receiving Social Security benefits can impact the overall retirement income strategy.
- Individuals should consider the role of Social Security in their retirement planning to make informed decisions about other savings and investment options.
