Kicking off with Understanding candlestick charts, this guide dives into the world of candlestick patterns, offering insights into their significance and how they are used in trading strategies. Get ready to unlock the secrets behind these powerful tools!
Candlestick charts have been around for centuries, originating in Japan and evolving into a popular method for analyzing financial markets. By understanding the components and patterns of candlesticks, traders can gain valuable insights into market trends and make informed decisions.
Introduction to Candlestick Charts
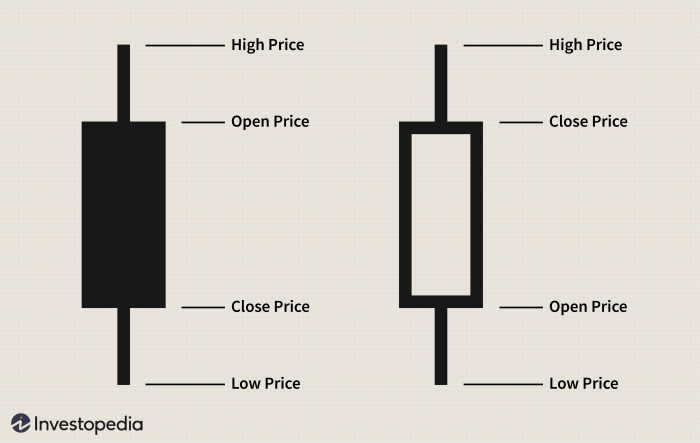
Candlestick charts are a type of financial chart used to represent the price movements of an asset over a specific time period. Each candlestick displays the open, high, low, and close prices for that period, providing a visual representation of market sentiment.
Components of a Candlestick
- The body of the candlestick represents the difference between the open and close prices. A filled (or red) body indicates a bearish movement, while a hollow (or green) body signifies a bullish movement.
- The wicks (or shadows) above and below the body show the high and low prices reached during the time period. They provide additional context about the price action and volatility.
Origin and History of Candlestick Charts
Candlestick charts originated in Japan in the 18th century and were used to track the price of rice. They were introduced to the Western world in the 20th century and have since become a popular tool for technical analysis in financial markets.
Types of Candlestick Patterns
Candlestick patterns are important tools used by traders to analyze market trends and make informed decisions. There are various types of candlestick patterns, each with its own significance. Let’s explore some common bullish and bearish candlestick patterns along with examples of reversal candlestick patterns.
Bullish Candlestick Patterns
- Bullish Engulfing: This pattern occurs when a small bearish candle is followed by a larger bullish candle that completely engulfs the previous candle.
- Hammer: A hammer candlestick has a small body and a long lower wick, indicating a potential reversal from a downtrend to an uptrend.
- Doji: A doji candle has an equal opening and closing price, signaling indecision in the market. When it appears after a downtrend, it can indicate a potential reversal.
Bearish Candlestick Patterns
- Bearish Engulfing: The bearish engulfing pattern is the opposite of its bullish counterpart, with a large bearish candle engulfing a smaller bullish candle.
- Shooting Star: A shooting star candlestick has a small body and a long upper wick, suggesting a potential reversal from an uptrend to a downtrend.
- Dark Cloud Cover: This pattern occurs when a bullish candle is followed by a large bearish candle that opens above the previous close and closes near the midpoint of the first candle.
Reversal Candlestick Patterns Examples
- Bullish Reversal: An example of a bullish reversal pattern is the Morning Star, which consists of a long bearish candle, followed by a small candle or doji, and then a large bullish candle.
- Bearish Reversal: An example of a bearish reversal pattern is the Evening Star, which comprises a large bullish candle, followed by a small candle or doji, and then a large bearish candle.
Reading Candlestick Patterns
Understanding how to read candlestick patterns is essential for successful trading. Candlestick wicks, colors, and trends provide valuable insights into market behavior.
Interpreting Candlestick Wicks
Candlestick wicks represent the high and low prices reached during a specific time period. A long wick indicates high volatility, while a short wick suggests stability. Traders use wicks to assess potential price reversals or continuations.
Significance of Candlestick Colors, Understanding candlestick charts
The colors of candlesticks play a crucial role in interpreting market sentiment. A green or white candle indicates a bullish trend, with prices closing higher than they opened. In contrast, a red or black candle signals a bearish trend, with prices closing lower than the opening.
Identifying Trends with Candlestick Patterns
By analyzing the sequence of candlestick patterns, traders can identify trends in the market. An uptrend consists of higher highs and higher lows, reflected in a series of bullish candlesticks. Conversely, a downtrend displays lower highs and lower lows, represented by bearish candlesticks.
Using Candlestick Patterns in Trading
Candlestick patterns are a valuable tool for traders to make informed decisions in the financial markets. By analyzing the patterns formed by the open, high, low, and close prices of an asset over a specific time period, traders can gain insights into market sentiment and potential price movements.
Combining Multiple Candlestick Patterns
When combining multiple candlestick patterns, traders look for confirmation signals to increase the reliability of their trading decisions. For example, if a bullish engulfing pattern is followed by a doji pattern indicating indecision, traders may wait for a confirmation in the form of a bullish marubozu candle to enter a long position.
Importance of Volume in Analyzing Candlestick Patterns
Volume is a critical component when analyzing candlestick patterns as it provides insight into the strength of a price movement. High volume accompanying a bullish pattern suggests strong buying pressure, increasing the likelihood of a bullish continuation. Conversely, low volume with a bullish pattern may indicate weak buying interest and potential trend reversal.
Candlestick Patterns for Technical Analysis: Understanding Candlestick Charts
Candlestick patterns are essential tools used in technical analysis to predict future price movements based on historical price data. By analyzing the shapes and formations of candles on a chart, traders can identify patterns that indicate potential entry and exit points in the market.
Spotting Potential Entry and Exit Points
- Look for reversal patterns like Doji, Hammer, and Shooting Star to signal potential trend changes.
- Identify continuation patterns such as Bullish and Bearish Engulfing patterns to confirm existing trends.
- Combine multiple candlestick patterns to increase the accuracy of your entry and exit decisions.
Tips for Using Candlestick Patterns Effectively
- Understand the psychology behind each candlestick pattern to interpret market sentiment accurately.
- Use candlestick patterns in conjunction with other technical indicators for confirmation signals.
- Practice recognizing candlestick patterns on historical charts to improve your pattern recognition skills.
